Friends who are engaged in operation know that there are various plans to write during the e-commerce operation process. For example, you often encounter the following dialogue scenarios at work:
Boss: "We want to build a community, you can write a community operation plan!"
Boss: "National Day is coming, we are going to do a National Day event and write me an event plan before tomorrow night!"
Employee: "I think our product is not very active recently, because... we can increase our activity in this way."
Boss: "Well, you have a good idea, please write a plan first!"
Boss: "We are going to go online recently, so you can write a mobile operation planning plan!"
Operations are basically a process of constantly writing plans, modifying plans, and implementing plans. Many friends may feel "blue and thin" or "shiitake mushrooms" when they hear the word "plan". Not to mention the change of plans until you want to die, the idea of starting to write plans is enough to torture the rhythm of you want to beat your boss.
Actually, is the plan really that difficult? Why do many of me rack their brains and still have no idea how to start until late at night? Or the plan is halfway through, and there is no idea, and then they begin to doubt the content of the first half.
The so-called plan is to make an idea and plan beforehand, with two purposes:
Let the leader know your ideas and ideas, whether your strategies are feasible, and whether there are loopholes in your ideas;
You can think twice before you act, and the later execution is orderly and well-founded.
Since the purpose of the plan is to sort out the work ideas or sort out the operation ideas and specific work plans in our operations, we must have a correct writing idea. The operation plan must be a process that is interlocking, the main logic must be clear, and the ideas and goals must be clear, so that you can write a high-quality operation plan with clear ideas.
1. Key ideas for writing a plan
The plan is used to sort out our ideas and guide our practice. We can recall that in fact, we will follow this key idea when doing anything:
In what context do you do this?
What is your purpose in doing this?
What goals do you use to measure the results of your doing this?
What is your specific execution strategy for doing this? That is, the clear schedule of people, things, wealth, resources, and time.
The background of the plan is to better clarify the purpose of your doing this, the purpose is to clarify the direction of your doing, the goal is to measure the effectiveness of your doing, and the strategy is to clarify how you should implement this matter, that is, who do you need? What does it take? How much budget does it take? How long does it take? What should you do at each stage?
The most critical step here is to clarify the purpose, because everything you need to do in the future is carried out around this purpose, and it is the direction of your work. If the purpose is wrong, then all the subsequent work will be wrong. So, before you do something or write a plan, you must be clear about what the purpose of doing it is.
2. Key thinking to use when writing a plan
Brother Chao mentioned an example in his article "Own experience tells you which is more important, thinking or experience?". If you associate the word "Apple", what will you think?
The wrong idea is to directly give the result words you think of, such as thinking of Apple computers, the apples you eat, and the iPhone. The result of this wrong thinking is that your thinking is confusing, and the final result is incomplete. Many people often have a smothered brain when doing things, and this is the key reason.
Let’s take a look at the correct idea. We can use the thinking disassembly method to think. The specific ideas are as follows:
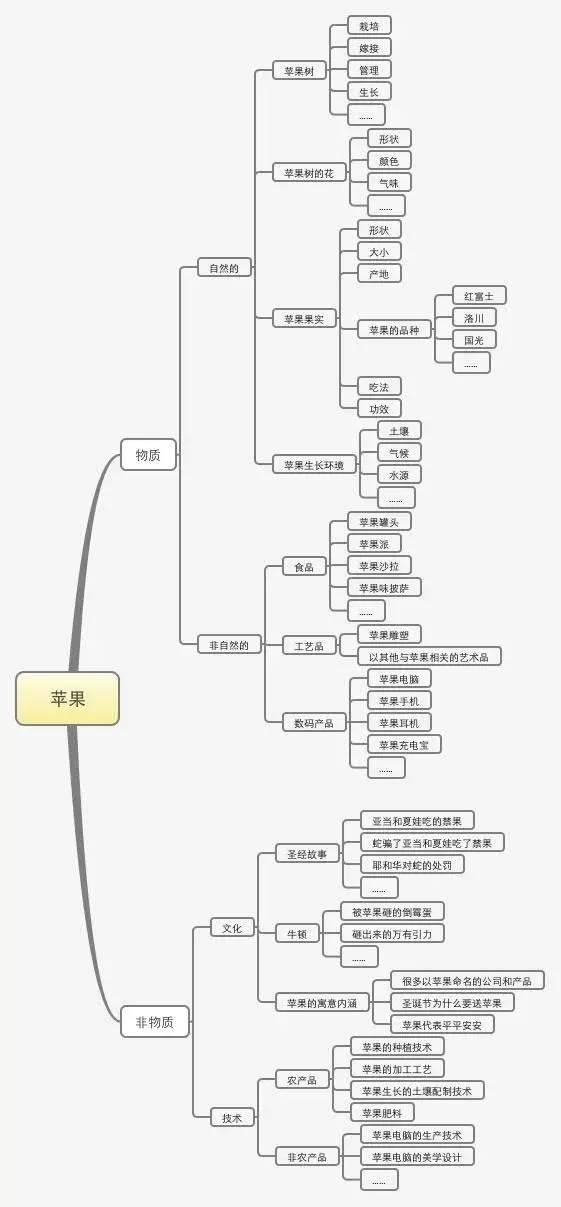
The above is a disassembly of the association ideas for the word "Apple". How to disassemble ideas and target disassembly in the actual operation process? We take the operation of self-operated e-commerce platform as an example. Brother Chao has never done e-commerce operations, but as long as the purpose is clear, his ideas are all understood. So here I try to use the method of thinking disassembly to sort out the ideas of e-commerce operations.
E-commerce companies should know that e-commerce has a universal formula: sales = traffic * conversion rate * customer unit price. The most direct purpose of e-commerce operations is to increase sales, and the goal is how much sales we need to increase? For example, if we increase sales by 10 million in a month, whether to achieve this goal is a basis and standard for measuring our operation. Of course, the formulation of goals must not be achieved by typing, and it needs to be calculated based on actual conditions.
Let’s first sort out the ideas:
Purpose : Increase platform sales
Target : Sales volume increase by 10 million in one month
Three factors affecting sales : traffic, conversion rate, and unit price (e-commerce universal formula)
First, based on the three factors that affect sales, we can split the work into three aspects:
Improve store traffic
Improve store conversion rate
Product pricing
Secondly, set goals and disassemble them according to the disassembly work. For example, in order to achieve a sales of 10 million, how much traffic should we attract, how much conversion rate of the platform should be increased? What kind of price promotion strategy should be adopted?
The goal for traffic can be split according to the channel, and the traffic targets are set for different channels at different stages according to the channel promotion effect.
In terms of improving the conversion rate of a store, we need to consider the influencing factors that affect the conversion rate, and then take corresponding measures around these influencing factors. For example, we can improve conversion rate through the following aspects:
Improve product packaging
Optimize the details page pictures
Optimize details page introduction document
Optimize the payment path and experience of consumers placing orders
Customer service order promotion skills
Do a good job in consumer evaluation management
Implement price promotion strategies, such as full discount, full discount, etc.
...
How to improve product packaging, product photography and picture processing, what kind of copywriting can better attract consumers, optimize orders and payment paths, how to improve customer service sales skills? User evaluation management skills and other specific optimization work involves the division of labor of personnel, and professionals do professional things. Of course, this is just an example of some of the work of e-commerce operations, because in actual operation, it also involves product category planning, store decoration, etc.
If you think carefully, you can find that if you clarify the above goals and goals, then break down the goals and goals, and then refine the specific strategies and work content based on the actual situation of the operation, and then further clarify the division of personnel, time node schedule, operation budget and required resource support, it is an e-commerce operation plan. Of course, this plan must not be imagined out of thin air like Brother Chao, just to give an example, but to formulate targeted measures based on the current status of the store and data analysis, but the specific ideas are similar.
The above ideas are also followed for product operation plans. You can recall the previous universal e-commerce formula: sales = traffic * conversion rate * customer unit price. If the average customer price is 0, that is, if we are operating a free product, then sales are also 0, because the direct purpose of operating a free product is not to increase sales, then the only thing we have to do is traffic * conversion rate. If our solution is for product recruitment, then the above formula becomes:
Registered user = traffic * conversion rate
Therefore, our work direction can be clearly defined in two directions:
Drainage (promotion)
Improve product registration conversion
Next, all the work can be carried out around two aspects: drainage and improvement of transformation.
Any plan is the same. The focus of making a plan is on the idea. When the background is clarified, first determine the purpose, then set the specific goal and disassemble it around the goal, and then determine the implementation plan. All the contents behind are carried out around the goal and goal. In the process of making plans, you can use the current mainstream idea sorting tools Xmind and Visio. These two tools can quickly help you sort out your idea system.
Taking the establishment of the operation process and standardization system as an example, this is a relatively large and relatively complex task. In practice, it is not as simple as thinking, because it involves various processes, specifications, rules, definitions, and various standardized template tables in operation work. So how should we start this work? What we still adopt is the previous idea disassembly method, which is simply disassembly as follows:
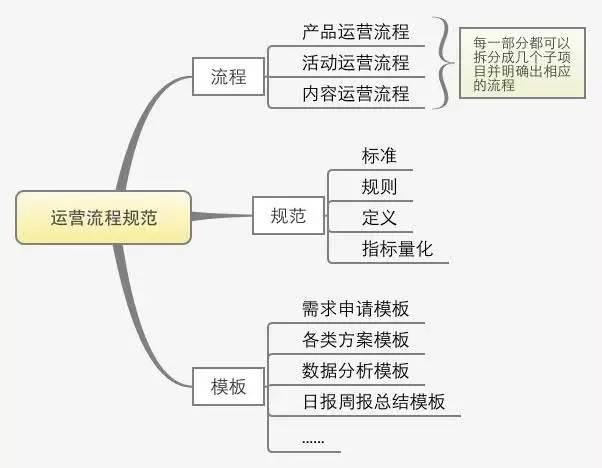
Unlike the activity plan, the "things" among the elements of "people", "things", "wealth", "resources" and "time" in the specific implementation strategy in the operation plan are relatively core. In the operation plan, it is necessary to plan for subsequent operation work from the "work" level.
We can still disassemble the "things" in the operation plan:
For any operational work, we can divide it into regular operational actions and unconventional operations. If it is an analogy, it is the relationship between health products and Viagra. Health products need to be taken in a long-term and fixed manner to improve body functions, and the efficacy of the medicine is relatively mild; Viagra is a strong medicine and a phased stimulus. In operation, regular operational actions and operation mechanisms are health care products that ensure users are constantly active, while irregular activities, product revisions, and improvements to large content strategies are Viagra that stimulates users in stages.
Therefore, the direction of implementing strategies in the operation plan has been basically clear, and it is divided into two aspects: routine operation work and unconventional operation work (generally belong to innovative work content).
Regular operation work is the establishment of a fixed operation mechanism, that is, the fixed work that operation personnel need to do every day, weekly, or regularly; unconventional operation work is some irregular innovative work. How to establish a conventional operation mechanism and what fixed normalization work should be done? What kind of activities or adjustments to product strategies can promote faster achievement of operational goals need to be carried out in combination with the actual operation status of the product.
The above-mentioned ideas need to be broken down according to one principle: exhaust each other and do not include each other. Here we will use the previous article "Thoughts + Steps + Methods, Three Steps to Teach you how to quickly build a user portrait?" as an example:
The division between explicit and implicit has been exhausted, which means that you cannot find the third latitude that is juxtaposed with it outside explicit and implicit. In terms of complementary inclusion, it means that the latitude of each level must be and relationship. If there is an inclusion relationship, it must be wrong. The inclusion and included relationship can only exist in the upper and lower latitudes.
3. Examples of plan writing ideas
When writing the plan, you must follow a principle concise, direct, and no nonsense.
A complete solution should include the following aspects:
1. Project background
Please do not make a long-term comment, and keep it within 3 items
2. Project Purpose
Direct purpose (there is only one and there can be only one, and all subsequent work must be carried out around this purpose)
Indirect purpose (no more than two related purposes, other related effects that can be brought about by doing this)
3. Project objectives
To make goals around goals, it must be quantified, which is the most direct measure for evaluating operational results.
This area can be used as an example. For example, a community positioning is a high school student user group, and all content focuses on high school students' learning and life exchanges. However, after users enter the university, the content of the community cannot meet the needs of this group of users entering the university. If we want to retain this group of users, we need to open a new section suitable for college students. Then the direct purpose here is very clear, which is to solve the problem of users' retention after graduating from high school. Therefore, when setting the target, the quantitative target can be set as follows:
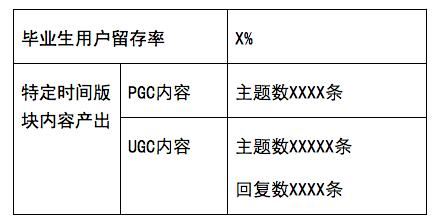
4. Operation strategy
If it is an activity plan, you need to include the activity object:
Activity time
Activities
Award settings
Activity Process
The corresponding copywriting content and material preparation.
If it is an operation plan, we will take the operation of the new community section as an example, including:
(1) Section positioning, content positioning
(2) Content operation
Content output method : PGC&UGC, as well as phased PGC and UGC output target planning, as well as UGC output sources and incentive methods. For example, how to select moderators and content output, interaction and section incentives, as well as motivation and promotion for expert users.
Section content specifications: Section posting and reply specifications, content management, etc.
User incentive system: such as member growth mechanism, incentive system, points, reward and punishment mechanism for posting replies, etc.
This part of the content can be divided into routine operation and unconventional operation. Due to time reasons, we will not divide it here, and only reminders are given here.
(3) Early promotion strategy
Such as key user invitation, section exposure, event promotion, etc.
(4) Early promotion plan
4. Plan for schedule
The purpose of the planning schedule is to clarify which person should do what at what time. This part of the time node, work matters and responsible persons must be clear.

5. Resource support
Promotion resources (resource location, promotion channels, etc.)
Requirements support (design requirements and development requirements)
Departmental support
...
6. Operational budget
This involves the formulation of cost budgets. For example, gold coins will be used as an incentive method during the operation of community operations or gold coin malls, so this part needs to be converted according to the proportion of gold coins being exchanged for RMB.
In this solution idea, purpose and goal are the most important. When writing a plan, of course it is also included in the specific operation work. You must clarify the purpose and confirm it with the boss, and carry out subsequent work when confirming that the purpose is correct.
The above introduces six aspects of the e-commerce operation plan. We need to learn to summarize, so that e-commerce operation will have good results!






![#Laogao E-commerce Newsletter# [E-commerce Morning News on January 5]](/update/1634606324l419797086.jpg)

![#Laogao E-commerce Newsletter# [February 6 E-commerce Morning News]](/update/1675647690l371436458.jpg)

 EN
EN CN
CN
